By Saeed Moradi, R&D Specialist - Innovation
Like other new technologies, exoskeletons are making their way into construction sites. Exoskeletons alleviate the strain of the jobs that include repetitive movements, heavy weightlifting and handling, and overexertion.
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSD) such as pain, numbness, and stiffness are common among construction workers. Some of these disorders can be irreversible in the long term. Based on the Bureau of Labor Statistics report, 36% of injuries involving missed workdays are caused by MSD like shoulder and back injuries. Exoskeletons can improve the ergonomics of work to limit the risk factors and increase the workers’ productivity. For example, they can help workers with inadequate physical capabilities to be able to perform heavy-duty tasks such as drilling and lifting.
What is Exoskeleton?
Exoskeleton or exosuit is one of the wearable technologies that are used to minimize tension and injury by providing joint support, weight distribution, and posture correction. An exoskeleton can be motorized or purely mechanical depending on the type and purpose. They are built of different kinds and provide support for various body regions.
Nowadays, exoskeletons are becoming more adjustable to fit the construction worker’s body and also in lighter weights to allow easier maneuvering in different tasks. They can be worn for the whole working day with less strain in doing repetitive tasks. In this article, we listed different types of exoskeletons that can be employed in construction jobs with their benefits and limitations.

Power gloves are worn around hand to help in gripping intensive and repetitive/static tasks such as lifting and holding heavy objects and tools. They are adjustable to hand size and required force to execute the tasks. Sensory equipment included in power gloves can perceive the pose and essential grip.
Pros
Cons
Adjustable size
Battery life
Force balance for each finger
Setup and calibration
More grip and power
May affect the precision

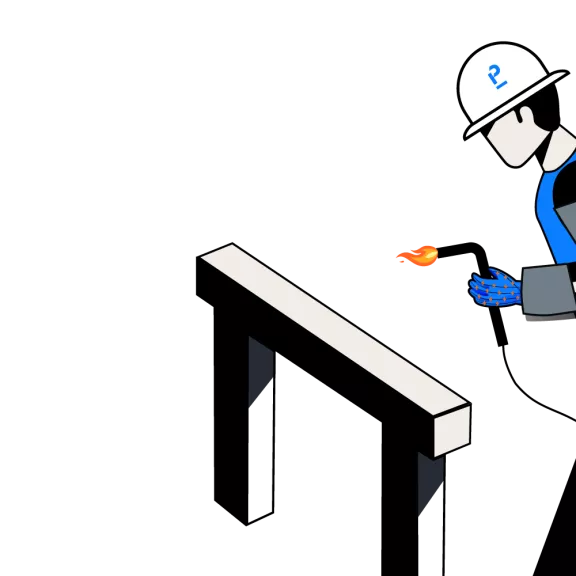
Arm and shoulder exoskeletons support upper body areas in lifting and holding heavy materials. Also, they can be used in repetitive arm movement and prolonged handling activities such as cutting, drilling, and scraping. There are several manufacturers providing arm and shoulder exoskeletons. They can weigh between 1.3 kg and 4 kg depending on their functionalities and they can fit the worker’s body to maximize movement and decrease the strain during job performance.
Pros
Cons
Relieves elbow and shoulder tension
Maintenance
Enhance control and precision
Move the force to lower body like waist
Water and dust proof
Easy movement
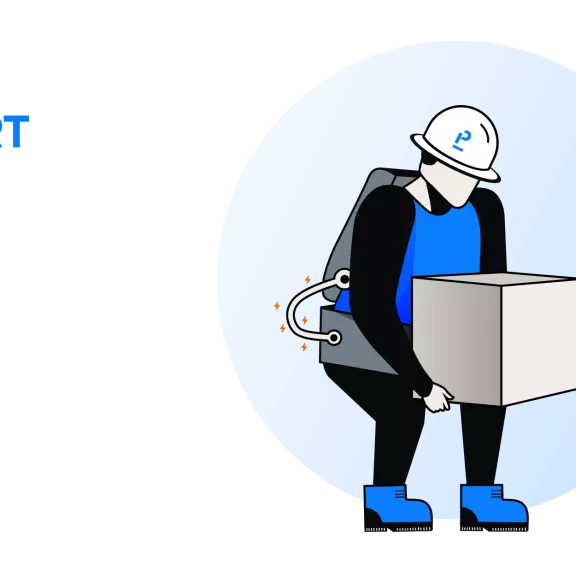

Back support exoskeleton covers body areas from shoulders to hips to diminish the force on back muscles while lifting heavy objects from below waist level and also while working in a forward-leaning posture. It corrects workers’ awkward pose and reduces the risk of disorders in the lower back.
Pros
Cons
Reducing the injuries from heavy lifting, static bending, asymmetric loads, long-standing position, and stooping.
Reducing the impact on the spine not the effort
Easy maintenance
Types with leg bounding may restrict movement
Water and dust proof

Leg support exoskeletons reduce strain because of standing and crouching postures. They reduce the stress on the knees and legs by transmitting the force directly to the ground. Long-standing and crouching positions happen a lot during various construction tasks such as installing electrical parts. These exoskeletons can lock in sitting pose as the chairs are not available on the job site because of safety and productivity considerations.
Pros
Cons
Supporting knee and leg joints
Limiting fast actions
Providing sitting support
Should choose proper size to fit
Can be well matched with shoulder and back support exoskeletons

Tool handling exoskeleton connects to heavy tools like drilling equipment and transfers the force and the load to its base which can be on the ground, scaffolding, or AWP. They can help workers to hold the tools for a longer time and increase accuracy and safety during task performance.
Pros
Cons
Holding heavy tools for a longer time
Limited tools on AWP
Reducing muscle fatigue and increasing the precision
Exoskeletons in action
Pomerleau as one of the pioneers in utilizing new technologies is using exoskeletons in its job sites. The aXLab, in a collaboration with researchers from Polytechnique Montréal, is studying the benefits and potential side effects of using exoskeletons for construction workers.
A survey was conducted to describe the experience of workers using arm and shoulder support exoskeletons made by Hilti to accomplish tasks like drilling and scraping on the job site. Based on the results of the survey on the impact on productivity and applicability of the exoskeletons, a series of benefits and drawbacks were listed. In general, exoskeleton provides support for the weight of the tools so fewer strain results, and productivity was improved. Also, the body movements were not limited, and the workers felt comfortable using an exoskeleton. On the contrary of what it seems, it is easy to put on and off the exoskeleton.
On the other hand, when the arms are elevated, it would be harder to control the tool vibration. For the jobs at an overhead level, the precision may be reduced because of being far from the point of the application of the force. Furthermore, many of the passive exoskeletons only support the weight of the tool and do not augment the force. Maintenance is another limitation since they required cleaning after using in a dusty environment.
There would be many criteria to consider in utilizing exoskeletons in construction job sites and it may affect the decision when selecting a proper exoskeleton for a construction task. Some aspects including:
- Working environment: dust, debris, work in height, required PPE during the work;
- Type of work: varying posture, duration of wearing, direction of movements, required force;
- Technological features: easy wearing and removal, on/off alternatives, movement angle, enforcement anchors.